Introduction
ISO 9001 standard sets out the criteria for a quality management system (QMS) and is released by
International Organization for Standardization (ISO). This standard encompasses best business practices and key
management principles including a customer focus, employee engagement, the process approach and continual improvement.
The latest edition was released in 2015 and it is referred as ISO 9001:2015
This standard uses the process approach and Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle with risk-based thinking for achieving enhanced performance.
Internal audits are conducted at planned intervals to ensure the conformance of QMS to the standard requirements as well as organizational own specific needs if any.
PDCA Cycle
PDCA (plan-do-check-act) is an iterative four-step management method used in business for the control and continual improvement of processes and products & services. All four stages are critical for ensuring effective and efficient way of working resulting in improved performance. There is a famous quote by Dr Deming (father of Quality Control) - In God We Trust, All Others Bring Data
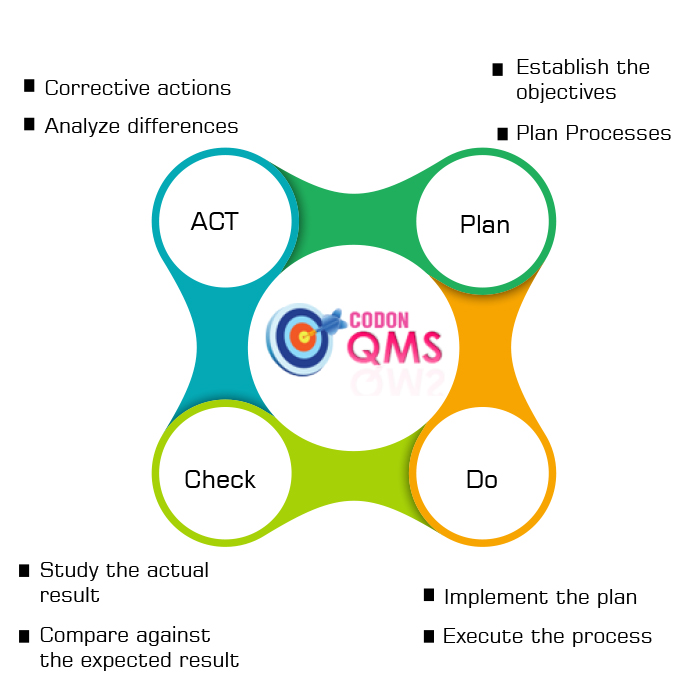
This is to emphasize the importance of the 'Checking' ie monitoring the performance & data collection and to 'Act' suitably where necessary.
This cycle is also called as Deming Cycle in reference to Dr Deming, who taught this concept to Japanese for building robust processes and continuous improvements during their quality revolution in 1950's.
Process Approach
A "Process" can be defined as a "Set of interrelated or
interacting activities, which transforms inputs into outputs". Inputs to a process are generally outputs of other processes.
The process approach means systematic definition and management of processes of an organization in an effective and efficient manner, so as to achieve the intended results with
the least possible wastage in the supply chain / value chain.
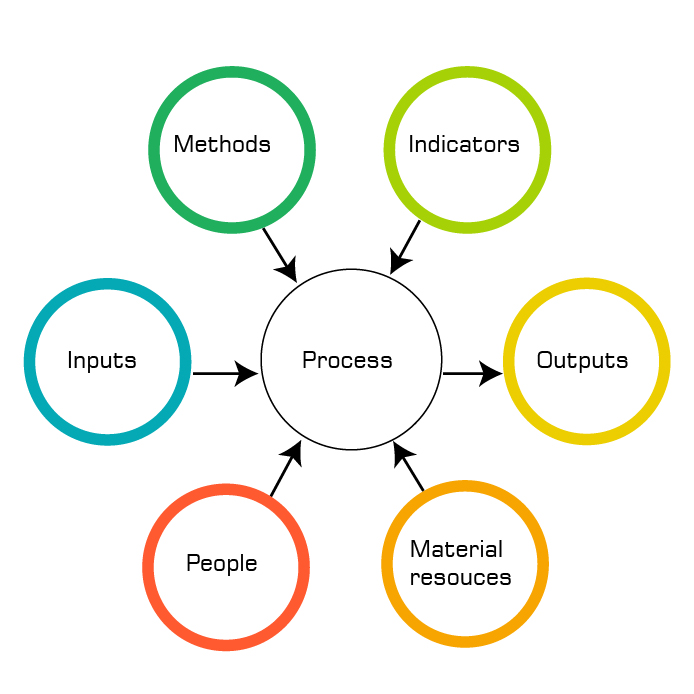
The process approach enables the organization to manage the interrelationships and interdependences among the processes of the system in a best possible way resulting in superior overall performance.
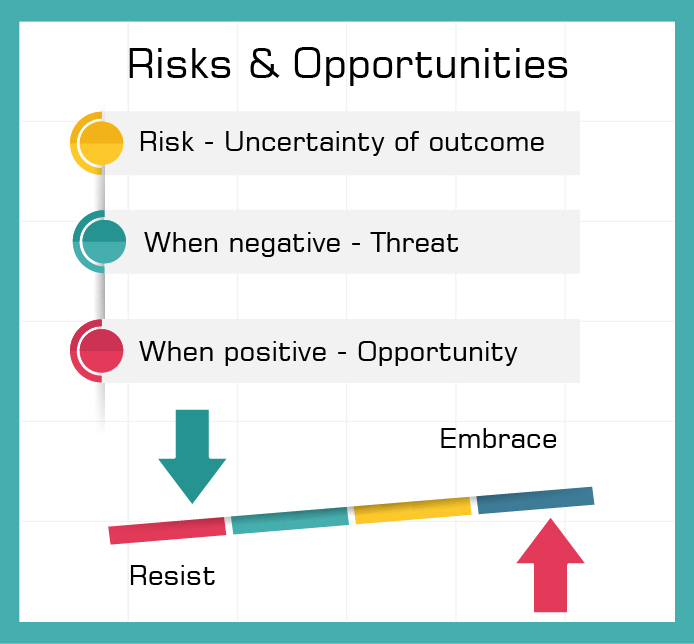
Risk Based thinking
The new standard also makes us to do risk based thinking there by addressing
risks and opportunities for achieving improved results and preventing negative effects.
As per ISO9001:2015, it is required to assess the risks and opportunities at planning stage and have actions to address them.
Risk is the effect of uncertainty that can have positive or negative effects resulting in opportunity for better performance (not all positive effects can give an opportunity) or threat for lower performance. The main aim of the risk based thinking is
to prevent the negative effects and enhance the performance where an opportunity exists in a systematic way.
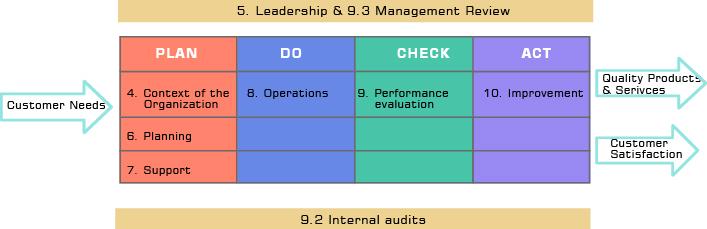
ISO 9001: 2015 standard requirements
| 1 | Scope | |
| 2 | Normative reference | |
| 3 | Terms & definitions | |
| 4 | Context of the organization | PLAN |
| 4.1 | Understanding the organization and its context | |
| 4.2 | Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties | |
| 4.3 | Determining the scope of the QMS | |
| 4.4 | QMS and its processes | |
| 5 | Leadership | PLAN |
| 5.1 | Leadership and commitment | |
| 5.2 | Policy | |
| 5.3 | Organizational roles, responsibilities and authority | |
| 6 | Planning | PLAN |
| 6.1 | Actions to address risks & opportunities | |
| 6.2 | Quality objectives and planning to achieve them | |
| 6.3 | Planning of changes | |
| 7 | Support | PLAN |
| 7.1 | Resources | |
| 7.2 | Competence | |
| 7.4 | Awareness | |
| 7.5 | Documented inforation | |
| 8 | Operation | DO |
| 8.1 | Operatinal planning and control | |
| 8.2 | Requirements for products & services | |
| 8.3 | Design & dev of P & S | |
| 8.4 | Control of externally provided processes, products and services | |
| 8.5 | Production and service provision | |
| 8.6 | Release of products and services | |
| 8.7 | Control of non-conforming outputs | |
| 9 | Performance evaluation | CHECK |
| 9.1 | Monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation | |
| 9.2 | Internal audits | |
| 9.3 | Management review | |
| 10 | Improvement | ACT |
| 10.1 | General | |
| 10.2 | Non-conformity and corrective actions | |
| 10.3 | Continual improvement |
Practicing this standard requirements shall drive quality culture across all levels of people at all activities in an organization resulting in doing things right all the time and improving performance from time to time.
Basic Statistical Techniques/ Quality Tools
The standard indicates the usage of statistical techniques for
performance data analysis. The 7 basic quality tools which comprises of graphical and basic
statistical techniques are most powerful in data capturing, analyzing and problem solving for effective process management & control.
Originally used for Quality performance analysis, evaluation & improvement in Japan and became very popular as 7 Basic Quality Tools or 7 QC tools.
The 7 basic tools are
- Cause & Effect diagram: (also called Ishikawa or fishbone chart): Identifies many possible causes for an effect or problem and sorts ideas into useful categories.
- Check sheet: A structured, prepared form for collecting and analyzing data; a generic tool that can be adapted for a wide variety of purposes.
- Control charts: Graphs used to study how a process changes over time.
- Histogram: The most commonly used graph for showing frequency distributions, or how often each different value in a set of data occurs.
- Pareto chart: Shows on a bar graph which factors are more significant.
the 80/20 rule - states that approximately 80% of the problems are created by approximately 20% of the causes. - Scatter diagram: Graphs pairs of numerical data, one variable on each axis, to look for a relationship.
- Flow chart - visual representation of the sequence of steps/activities/actions and decisions needed to perform a process.